Introduction: Indigenous Languages
Indigenous languages are a fundamental part of the cultural identity and intangible heritage of the native peoples of the Amazon. Each language encapsulates a unique worldview, a distinct relationship with nature, and a wealth of knowledge passed down through generations. Napo Cultural Center is dedicated to the preservation and revitalization of indigenous languages, recognizing their importance for cultural diversity and community identity. This article explores how the center promotes the conservation of indigenous languages and their relevance in modern society.

The Cultural Value of Indigenous Languages
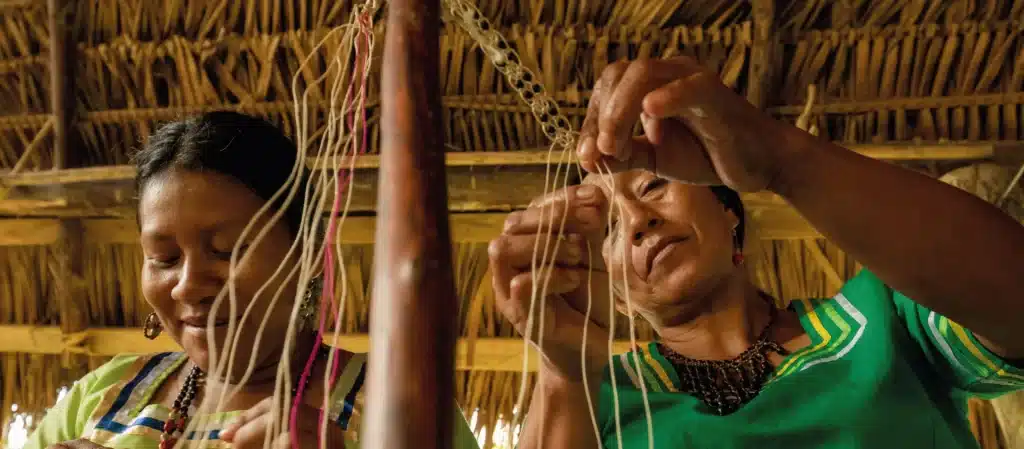
Indigenous languages are not merely tools for communication; they are carriers of stories, traditions, and ancestral knowledge. Through language, myths, legends, and knowledge about traditional medicine and natural resource management are transmitted. At Napo Cultural Center, preserving languages like Kichwa is deeply valued, as each word and expression reflects a unique connection with the Amazon’s natural and spiritual environment. The loss of a language is not just the loss of words but the disappearance of a worldview.
Language Revitalization Programs
Napo Cultural Center has implemented specific programs to revitalize indigenous languages, focusing on the teaching and promotion of Kichwa among new generations. Through language workshops, classes in local schools, and educational materials, the center seeks to encourage the use of Kichwa in both daily life and formal educational settings. These programs focus not only on grammar and vocabulary but also on the culture and stories that accompany the language, ensuring a comprehensive understanding of its importance.
Bilingual Education in the Community
Bilingual education is essential for the preservation of indigenous languages. At Napo Cultural Center, an educational approach is promoted that includes both Kichwa and Spanish, providing children and young people with the skills to communicate in both languages. This approach not only strengthens cultural identity but also prepares students to interact in a globalized world without losing their roots. Bilingual education is seen as a key tool for community empowerment and the protection of cultural heritage.
Community Involvement in Language Preservation
Preserving indigenous languages is a community effort, and Napo Cultural Center works closely with community leaders and elders to ensure the transmission of linguistic knowledge. Elders play a crucial role as keepers of language and culture, and their involvement in revitalization programs is essential. By creating spaces for storytelling, traditional songs, and cultural practices, active community participation in preserving their language is encouraged.
Technology and Language Preservation
Napo Cultural Center also explores the use of technology as a tool for language preservation. The creation of mobile applications, online dictionaries, and audio and video recordings in Kichwa are some of the initiatives being carried out to document and disseminate the language. These digital tools not only preserve the language for future generations but also make it accessible to a broader audience, promoting recognition and respect for linguistic diversity.
Conclusion
The preservation of indigenous languages is crucial for cultural diversity and the identity of Amazonian peoples. Through revitalization programs, bilingual education, community involvement, and the use of technology, Napo Cultural Center is committed to protecting and promoting languages like Kichwa. These efforts not only ensure the continuity of indigenous languages but also strengthen the communities’ connection to their cultural and natural heritage, ensuring that their legacy endures for future generations.